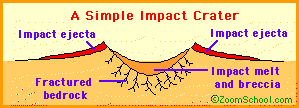
 When meteorites
hit the Earth they cause a crater to form. The bigger the meteorite, the bigger
the crater.
When meteorites
hit the Earth they cause a crater to form. The bigger the meteorite, the bigger
the crater.A meteor shower is a phenomenon in which many meteors fall
through the atmosphere in a relatively short time and in approximately parallel
trajectories. A very intense meteor shower is called a meteor storm.
Meteor showers (and storms) occur when the Earth passes through a comet's orbit,
and left-over comet debris (rocks, etc.) bombards the Earth. Each meteor shower
occurs at a predictable time each year.
METEORITES
A meteorite is a meteor that has fallen to Earth. At least 100 meteorites hit
the Earth every year. Meteorites have survived a fiery fall through the Earth's
atmosphere and have lost a lot of mass in that process. Most meteorites burn up
in the Earth's atmosphere; all that is left is a bit of dust. Every day, about
3000 tons of meteoroid dust falls to Earth.
 When meteorites
hit the Earth they cause a crater to form. The bigger the meteorite, the bigger
the crater.
When meteorites
hit the Earth they cause a crater to form. The bigger the meteorite, the bigger
the crater.